Eye Doctor Explains What To Do If You Start Seeing ‘Floaters’
Eye floaters are a common visual phenomenon that many people experience at some point in their lives. While they are often harmless, a sudden increase in floaters can sometimes indicate a more serious eye condition. In this article, we will explore what floaters are, their causes, when to seek medical attention, available treatments, and preventive measures to maintain good eye health.
What Are Eye Floaters?
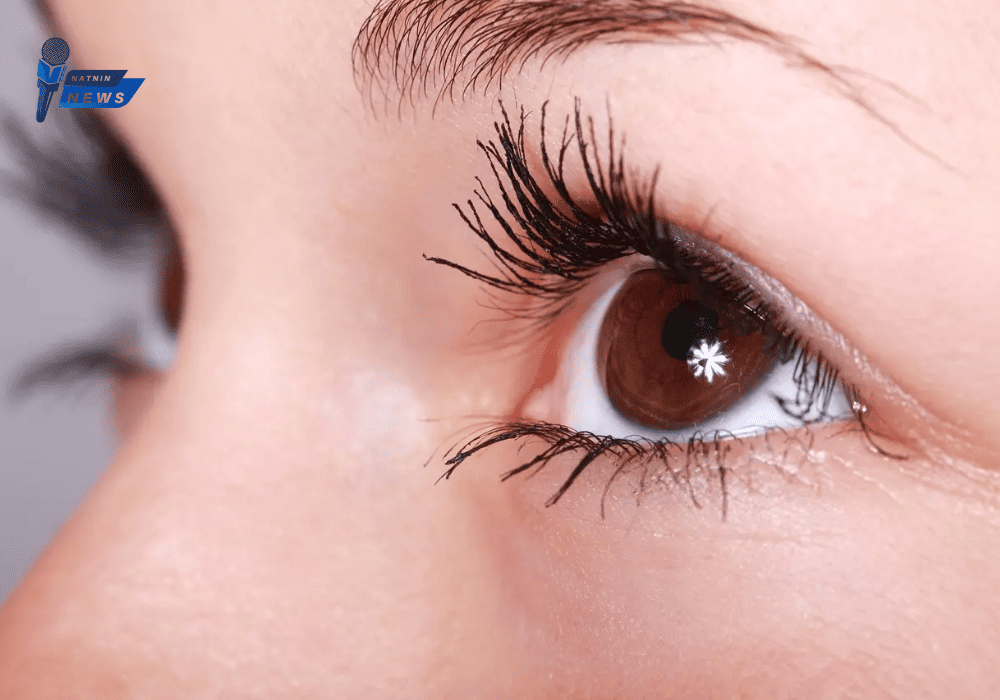
Eye floaters appear as tiny spots, specks, or thread-like strands that drift across your field of vision. They move as your eyes move and may seem to dart away when you try to look at them directly. These floaters are most noticeable when looking at a bright, plain background, such as a blue sky or a white wall.
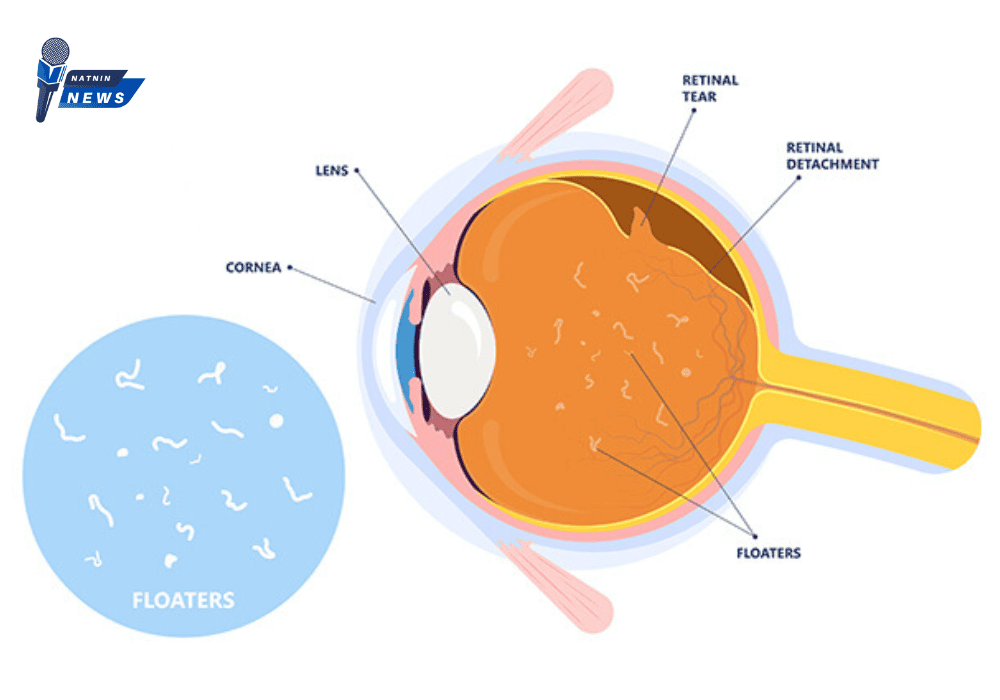
Floaters form when tiny pieces of the vitreous, the gel-like substance inside the eye, clump together. These clumps cast shadows on the retina, creating the illusion of floating objects in your vision. Although they may seem to be outside the eye, floaters are actually inside the eye itself.
Are Eye Floaters Normal?
For most people, floaters are a natural part of aging. They tend to develop gradually and do not usually cause significant vision problems. However, if you suddenly notice a large number of floaters, flashes of light, or a dark curtain over part of your vision, it could indicate a serious eye condition that requires immediate medical attention.
Common Causes of Eye Floaters
Several factors can contribute to the appearance of eye floaters. Understanding the causes can help determine whether they are harmless or require urgent treatment.
1. Aging and Changes in the Vitreous
As we age, the vitreous gel inside the eye begins to shrink and liquefy. This natural process causes tiny collagen fibers to clump together, resulting in floaters. This is the most common cause of floaters and is usually harmless.
2. Posterior Vitreous Detachment (PVD)
PVD occurs when the vitreous gel pulls away from the retina. This is a common condition in people over 50 and can cause a sudden increase in floaters. In most cases, PVD is not dangerous, but it can sometimes lead to retinal tears or detachment.
3. Retinal Tears or Detachment
A retinal tear occurs when the shrinking vitreous pulls too hard on the retina, creating a small tear. If left untreated, fluid can seep through the tear, causing the retina to detach from the back of the eye. This is a medical emergency that requires immediate treatment to prevent permanent vision loss.
4. Eye Injuries
Trauma to the eye, such as a direct hit or an accident, can cause damage to the vitreous or retina, leading to the sudden appearance of floaters.
5. Inflammation (Uveitis)
Inflammation inside the eye, particularly in the uvea (the middle layer of the eye), can cause floaters. Conditions such as posterior uveitis can lead to inflammation of the vitreous, resulting in floaters and blurred vision.
6. Diabetic Retinopathy
People with diabetes are at risk of developing diabetic retinopathy, a condition in which damaged blood vessels leak fluid or blood into the vitreous. This can lead to floaters and vision problems.
7. Eye Surgeries and Medications
Certain eye surgeries, such as cataract removal, can cause temporary floaters. Additionally, some medications injected into the vitreous cavity can lead to air bubbles that appear as temporary floaters.
When Should You See an Eye Doctor?
Although spots in your vision are usually harmless, there are situations where they may signal a more serious problem. You should see an eye doctor immediately if you experience:
- A sudden increase in the number of moving specks.
- Flashes of light in your peripheral vision.
- A dark shadow or curtain blocking part of your vision.
- A sudden loss of vision in one or both eyes.
- Blurred or distorted vision that does not improve.
These symptoms could indicate a retinal tear or detachment, which requires urgent treatment to prevent permanent vision loss.
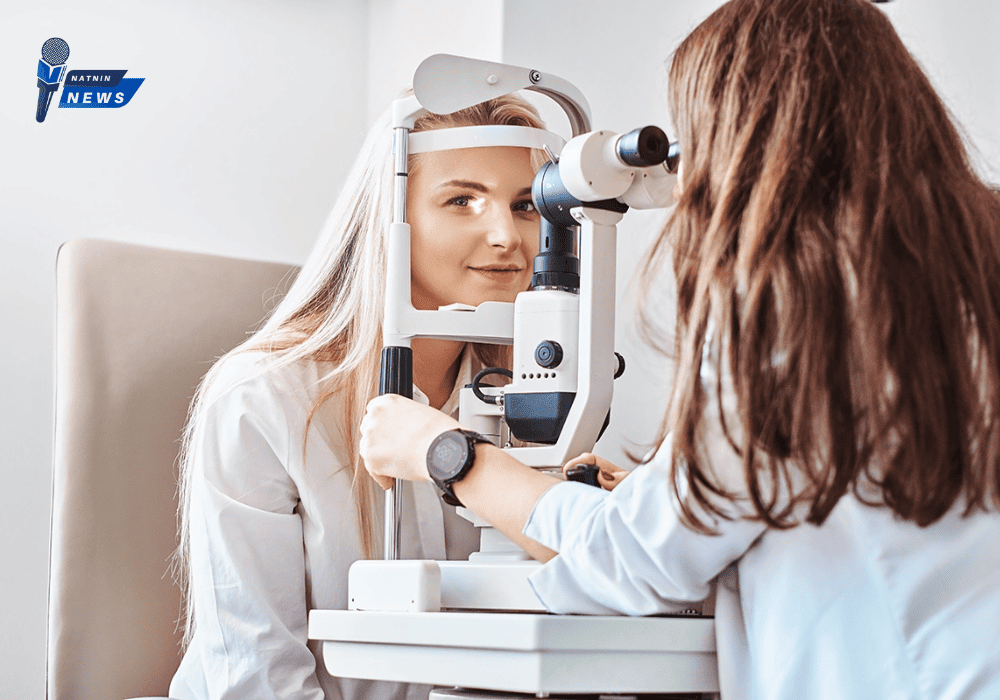
How Are Visual Disturbances Diagnosed?
An eye doctor can diagnose unusual visual changes through a comprehensive eye exam, which may include:
- Dilated Eye Exam – Drops are used to widen the pupil, allowing the doctor to examine the retina and vitreous for abnormalities, retinal tears, or detachments.
- Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) – This imaging test provides a detailed view of the retina to detect irregularities.
- Ultrasound Imaging – If the vitreous is too cloudy to see the retina clearly, ultrasound may be used to check for retinal detachment.
Treatment Options for Visual Obstructions
1. Observation and Monitoring
If these visual changes are mild and do not significantly affect vision, no treatment is needed. Most people learn to ignore them, and over time, they may settle at the bottom of the eye, becoming less noticeable.
2. Laser Vitreolysis
Laser therapy can break up large obstructions, making them less noticeable. This procedure is safe but may not be effective for everyone. It is generally recommended for severe cases that interfere with daily activities.
3. Vitrectomy (Surgical Removal)
In severe cases where vision is significantly impaired, a vitrectomy may be performed. This surgery involves removing the vitreous gel and replacing it with a saline solution. Although effective, this procedure carries risks such as retinal detachment, infection, and cataract formation.
Can Vision Issues Be Prevented?
While you can’t completely prevent these visual disturbances, maintaining good eye health can reduce the risk of serious eye conditions. Here are some preventive measures:
- Eat a nutrient-rich diet – Foods high in vitamins A, C, and E, along with omega-3 fatty acids, help support eye health.
- Stay hydrated – Drinking enough water keeps the vitreous gel in good condition.
- Protect your eyes – Wear sunglasses to shield your eyes from harmful UV rays and protective eyewear in risky situations.
- Manage underlying health conditions – If you have diabetes or high blood pressure, keeping them under control can help prevent eye complications.
- Have regular eye exams – Routine checkups help detect eye problems early before they become serious.

Conclusion
Floaters are a common visual occurrence, especially as we age. While they are usually harmless, a sudden increase in floaters, flashes of light, or vision loss can indicate a serious problem such as retinal detachment. If you experience any of these symptoms, seek immediate medical attention to prevent potential vision loss. By maintaining good eye health and getting regular eye checkups, you can ensure that your vision remains clear and healthy.
Learn what causes floaters in your vision and when to see an eye doctor. Discover symptoms, treatments, and prevention tips for eye floaters to maintain good eye health.
Follow us for useful information that helps your life: https://www.facebook.com/LilMissLoveless/