🌿 Bright, bold, and brimming with traditional healing power, Greater Celandine (Chelidonium majus) has long held a place in European and Asian herbal medicine. With its cheerful yellow blossoms and signature orange sap, this plant is as striking visually as it is medicinally.
Often dubbed “wartweed”, greater celandine is celebrated for supporting liver health, calming digestive distress, and topically removing skin growths like warts. But despite its wide-ranging benefits, it must be used with care due to its potent bioactive compounds.
Let’s uncover the 10 key benefits of Greater Celandine, how to use it safely, and important precautions to keep in mind.
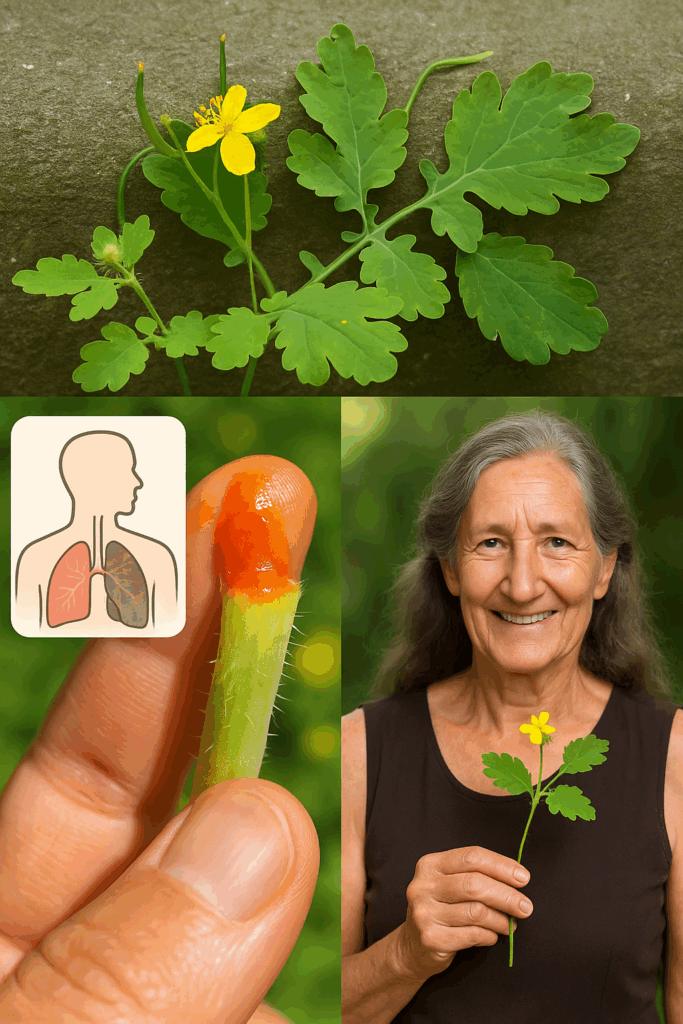
🌿 What Makes Greater Celandine Special?
Greater Celandine contains powerful isoquinoline alkaloids such as chelidonine, sanguinarine, and berberine. These compounds are responsible for its therapeutic actions—but also its potential toxicity. The plant is most commonly used to support:
- Liver and gallbladder function
- Skin health and wart removal
- Digestive balance
- Immune support through antimicrobial activity
✅ 10 Health Benefits of Chelidonium majus
1. 🧪 Supports Liver and Gallbladder Function
Greater celandine has long been used to stimulate bile flow, improve detoxification, and relieve discomfort caused by gallstones or sluggish liver activity.
2. 🌱 Eases Digestive Discomfort
Thanks to its antispasmodic properties, it can relieve IBS, cramping, indigestion, and bloating by relaxing smooth muscles in the digestive tract.
3. 🌼 Removes Warts and Skin Growths
The orange latex sap is traditionally applied to warts, corns, and calluses. Its keratolytic and antiviral effects gradually break down abnormal skin tissue.
4. 🔥 Reduces Inflammation
The plant’s anti-inflammatory alkaloids help relieve mild joint pain, stomach inflammation, and skin irritation when used topically or internally in small doses.
5. 🦠 Antimicrobial Action
Greater celandine is naturally antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal, making it useful for addressing infections both externally and internally.
6. 🌬️ Soothes Respiratory Conditions
Used in traditional medicine to clear phlegm and relieve bronchitis, asthma, or persistent coughs by reducing mucus buildup and relaxing airways.
7. 🧹 Aids in Whole-Body Detox
Often found in detox teas and tinctures, it supports liver drainage and toxin elimination, especially when combined with other detoxifying herbs.
8. 🧬 Shows Anticancer Promise
Some alkaloids in Chelidonium, like chelidonine, have been studied for their potential anticancer properties, particularly in slowing cell proliferation. However, more research is needed.
9. 🤕 Offers Mild Pain Relief
Greater celandine exhibits analgesic properties, especially for digestive or gallbladder-related pain.
10. 👁️ Traditional Eye Care
Folk medicine sometimes used diluted infusions of the plant to soothe eye irritation and minor infections, though modern use should be cautious and physician-guided.
🍵 How to Use Greater Celandine
1. Infusion or Tea (Liver and Digestion Support)
Ingredients:
• 1 tsp dried aerial parts
• 1 cup boiling water
Instructions:
Steep for 10 minutes, strain, and drink once daily. Avoid extended use beyond 7–10 days unless supervised by a practitioner.
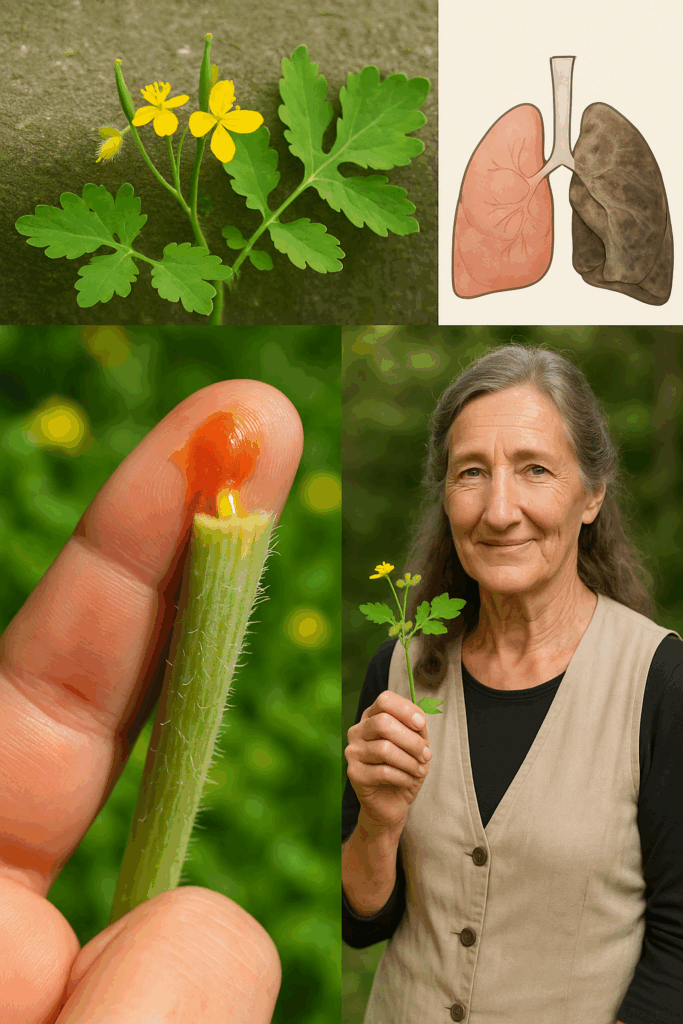
2. Topical Sap (Warts and Skin Tags)
Break a fresh stem and apply the orange sap directly to the wart once daily. Avoid use on healthy skin, open wounds, or large areas.
3. Tincture (Concentrated Internal Use)
Take 5–15 drops of tincture in water up to 3 times daily, preferably under professional guidance. Tinctures are potent and best reserved for liver or bile flow support.
4. Capsules or Extracts (Standardized Dosing)
Capsules may contain controlled doses of the herb’s active compounds, offering liver support or detox benefits with a reduced risk of overdose. Use as labeled or under supervision.
⚠️ Precautions and Safety Considerations
🚨 Use with Caution. Greater celandine is powerful—and not without risks.
- Toxic in high doses. Its alkaloids can cause liver toxicity, nausea, vomiting, or nervous system issues when overused.
- Skin irritation possible. The sap can cause burning or dermatitis on sensitive skin.
- Avoid during pregnancy and breastfeeding. It has not been proven safe and may stimulate uterine contractions.
- Not for long-term use. Limit internal use to short cycles (1–2 weeks), with breaks in between.
- Drug interactions. May interfere with medications for the liver, gallbladder, or cardiovascular system.
🧠 Final Thought: Potent Plant, Ancient Wisdom
Greater Celandine is a classic example of a “double-edged” medicinal herb—immensely beneficial when used with respect and moderation, yet potentially harmful if misused.
From cleansing the liver to clearing warts, its therapeutic potential is vast. But always approach it with knowledge, guidance, and care. When used responsibly, Chelidonium majus can be a transformative addition to a holistic health regimen.
💬 Use the wisdom of the past—but always pair it with the caution of today.


