In the pursuit of a greener, more resilient agricultural future, one surprising yet powerful ally is emerging from the world of weeds — the stinging nettle (Urtica dioica). Long dismissed as a garden nuisance, nettles are now gaining recognition for their exceptional agricultural value. When transformed into a fertilizer and pesticide, nettles offer a dual-function solution that supports plant nutrition and pest control — all without synthetic chemicals.
Here’s how nettle fertilizer pesticide can redefine eco-friendly farming.

🌱 The Versatility of the Nettle Plant
Nettle (Urtica dioica) is a hardy plant found across Europe, Asia, the Americas, and Africa. While its stinging hairs have made it infamous, it holds incredible potential for soil enrichment and plant protection.
Nutrient Powerhouse:
Nettles are rich in:
- Nitrogen (N) – Boosts leafy growth
- Potassium (K) – Supports flowering and fruiting
- Calcium (Ca) – Strengthens cell walls
- Iron (Fe) – Aids in chlorophyll production
Natural Pesticidal Properties:
Nettles contain natural defensive compounds like:
- Formic acid – Insect-repelling
- Lectins and histamines – Natural irritants to pests
These traits make nettles an ideal ingredient for a pesticide-fertilizer hybrid that’s both effective and safe for the environment.
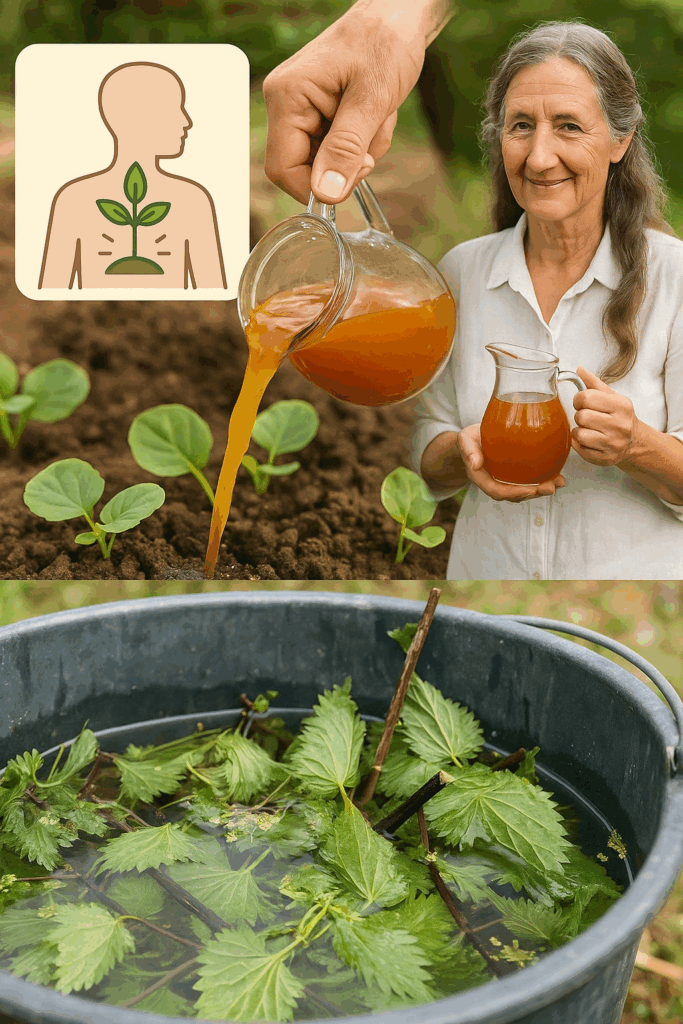
🧪 How to Make Nettle Fertilizer Pesticide
Creating nettle fertilizer is simple and cost-effective — perfect for both home gardeners and large-scale farms.
🌿 Ingredients:
- Fresh nettle leaves and stems (avoid flowering parts)
- Large bucket or container with lid
- Clean, non-chlorinated water
🧴 Instructions:
- Harvest Nettles: Use gloves and clippers to collect healthy, green nettles.
- Chop: Cut them into smaller pieces to accelerate fermentation.
- Soak: Fill the container with the nettles and water (roughly 1:10 by weight).
- Ferment: Cover and allow to steep for 1–2 weeks. Stir daily. It will darken and develop a strong smell — a sign of nutrient release.
- Strain: Filter out solids and store the liquid.
- Dilute: For application, dilute the liquid 1:10 with water.
🌾 Application Methods
1. Foliar Spray:
Spray diluted solution directly on leaves for quick nutrient absorption and to deter aphids, mites, and fungal spores.
2. Soil Drench:
Pour around the base of plants to enrich soil, stimulate root growth, and enhance nutrient uptake.
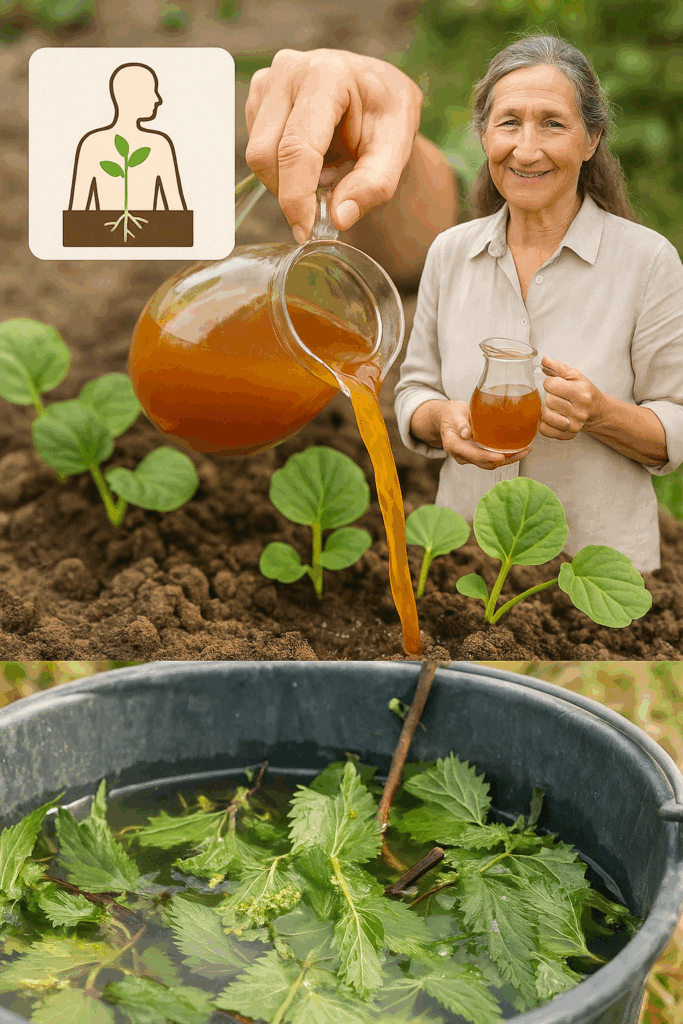

🌍 Key Benefits of Nettle Fertilizer Pesticide
✅ Environmentally Friendly
Free from synthetic chemicals, nettle fertilizer reduces toxic runoff and preserves beneficial insects.
💸 Low-Cost and Accessible
Nettles grow abundantly and don’t require processing equipment, making them a budget-friendly option for small farmers and home growers.
🌿 Improves Plant Resilience
Regular application strengthens plants, making them more resistant to pests, diseases, and drought.
🚫 Reduces Chemical Dependency
Supports a chemical-free growing environment, helping restore biodiversity and soil microbiota.
🌱 Enhances Soil Health
Fermented nettle fertilizer contributes organic matter and microbes, improving soil structure, aeration, and fertility over time.
🧭 A Step Forward in Regenerative Agriculture
In a world shifting toward climate-conscious farming, nettle fertilizer pesticide offers a practical and regenerative solution. It empowers farmers to work with nature, not against it, by leveraging the natural chemical defenses and nutrient profile of a wild plant.
Whether you’re managing a community garden or a commercial farm, incorporating nettle fertilizer into your routine can help:
- Cut costs
- Reduce ecological impact
- Build long-term soil health
⚠️ Pro Tip:
Use non-metallic containers during fermentation to avoid chemical reactions. Always wear gloves when harvesting to prevent stings. Apply during early morning or late afternoon to prevent leaf scorch.
🌿 Final Thought
The transformation of nettles from weed to wonder crop input is a testament to how nature offers sustainable answers in plain sight. Simple, powerful, and profoundly effective, nettle fertilizer pesticide represents a cornerstone of regenerative agriculture and is a practical step toward a more self-sustaining farming future.
Harness the sting — and grow sustainably.